RA1, RA2, and R3B are rules for reflective traffic signs in the UK. Each rule means a different amount of reflectivity. This helps drivers see signs well in any weather. Reflective signs are very important for stopping accidents. They help most at night or when the weather is bad. UK rules say road signs must use special reflective materials. These materials must follow strict rules to keep people safe. Using the right reflective sheeting follows the law. It also helps drivers stay in their lanes. Drivers can spot dangers faster with the right signs.
At OPTRAFFIC, we provide a range of reflective traffic signs that meet UK standards, including RA1, RA2, and R3B. Our high-quality materials ensure maximum visibility and safety for drivers, helping to reduce accidents and keep roads safer. Explore our range today to ensure compliance and enhance road safety.
Key Takeaways
- Reflective sheeting lets drivers see signs at night. It also helps in bad weather. This makes roads safer for everyone.
- RA1, RA2, and R3B are UK rules for reflective materials. Each one gives different levels of brightness and strength.
- RA1 works well on quiet roads with slow cars. RA2 is good for main roads and busy streets. R3B is best for motorways and fast roads.
- The law says you must use the right reflective sheeting. This helps stop accidents by making signs easy to see from far away.
- Signs need to be checked and fixed often. This keeps them bright and working well. It also helps them meet safety rules and last longer.
Reflective Traffic Signs in the UK

What is Reflective Sheeting?
Reflective sheeting is a special material for traffic signs. It helps road signs shine when light hits them. This material covers many traffic signs in the UK. It works by bouncing car headlights back to drivers. This makes signs easy to see at night or in low light. There are different types of reflective sheeting. Engineer Grade uses tiny glass beads to reflect light. High-Intensity Prismatic sheeting uses small prisms to make signs brighter. Diamond Grade sheeting uses advanced microprisms for the brightest signs. Some road signs use fluorescent reflective sheeting. This type uses special colours to make signs brighter in the day and at dusk. These materials help drivers see important information quickly, even in fog or rain.
| Type of Reflective Sheeting | Technology Used | Typical Use | Reflectivity Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engineer Grade | Glass bead | Street name signs, non-critical | Moderate |
| High-Intensity Prismatic | Microprismatic lenses | Warning and regulatory signs | High |
| Diamond Grade | Cubic corner microprism | Motorway and critical road signs | Very High |
| Fluorescent Reflective | Special pigments | School zones, sharp bends, work areas | Enhanced |
Why Reflectivity Matters
Reflectivity is very important for road safety. Reflective traffic signs help drivers see and read signs clearly. This is helpful when it is dark or raining. Good reflectivity lets drivers spot signs from far away. This gives them more time to react and stay safe. Studies show that bright signs with fluorescent sheeting can lower crashes by up to 40% at crosswalks and 35% on rural roads. UK rules say road signs must be easy to see in all weather and light. Reflective materials help signs stand out at night and in bad weather.
Tip: Reflective traffic signs with high reflectivity help older drivers and people with weaker eyesight by making signs easier to see.
Tests show that reflective signs can be seen from over 170 metres away. Non-reflective signs can only be seen from less than 40 metres. This extra distance gives drivers more time to slow down or change lanes. Reflectivity also helps drivers react faster and avoid accidents. Using the right retroreflective sheeting keeps everyone safer on the road, day and night.
Reflectivity Standards and Their Development
Early Traffic Sign Visibility
Long ago, UK traffic signs used paint or metal, which made them hard to see at night. In the 1930s, engineers experimented with new ideas by mixing glass beads into wet paint. This caused the signs to shine when headlights hit them. By the late 1940s, engineers developed a new sheeting with glass beads, making signs brighter and easier to see in low light. In the late 1950s, engineers introduced engineer-grade sheeting, which had glass beads inside a clear layer, improving the durability and brightness of the signs. In the early 1970s, high-intensity sheeting became common, making signs easier to see and lasting up to ten years. And in the late 1980s, engineers invented microprismatic technology, using tiny prisms to reflect more light, which made signs much brighter and visible from greater distances.
| Period | Milestone Description |
|---|---|
| 1930s | Glass beads on wet paint for reflectivity. |
| Late 1940s | Exposed glass bead retroreflective sheeting introduced. |
| Late 1950s | Engineer-grade sheeting with embedded glass beads. |
| Early 1970s | High-intensity sheeting for improved visibility and durability. |
| Late 1980s | Microprismatic technology for superior reflectivity and visibility. |
Setting the Standards
As signs improved, the UK established clear rules. The TSRGD and BS EN 12899-1:2007 are the main standards for road signs. These rules set three classes: Class RA1, Class RA2, and R3B. Each class uses different technology tailored to specific types of roads. Class RA1 uses glass beads and is ideal for quieter roads. Class RA2 utilizes microprismatic technology, which nearly doubles the brightness of signs. As a result, drivers can see these signs from up to 250 meters away. R3B, on the other hand, uses advanced microprismatic technology, making it the brightest and longest-lasting option. It is used on motorways and overhead signs. Furthermore, the rules specify that signs must be regularly checked and maintained to stay in good condition. Microprismatic retroreflective sheeting has become the most effective technology, ensuring that the UK can keep roads safe for everyone.
RA1, RA2, and R3B Reflective Materials
RA1 Reflective Overview
The most basic type of reflective sheeting for UK road signs is RA1. It uses glass beads to send car headlights back to drivers. You will see class ra1 signs on quiet streets and private roads. These signs are not used on motorways or busy dual carriageways. RA1 reflective works best where there are street lights and cars go slowly.
- RA1 reflective saves money for councils and builders.
- It gives enough brightness where signs do not need to stand out.
- You often see RA1 reflective on signs in towns and city streets.
The Department for Transport states that RA1 reflective must meet a brightness of at least 75 cd/m²/lux. Weather and damage can reduce its brightness over time, so regular checks are necessary. RA1 reflective works well for signs that do not need to be visible from long distances or in poor lighting conditions.
Note: RA1 reflective is not good for motorways or risky places, because it is not bright enough for fast cars.
RA2 Reflective Overview
RA2 reflective sheeting is brighter and lasts longer than RA1. It uses better glass beads or microprisms to reflect more light. RA2 reflective is used for most main road signs in the UK. Class ra2 signs are found on busy roads and places where cars go faster. RA2 reflective is great for warning signs and speed limits.
| Parameter | RA1 (Type A) | RA2 (Type B) |
|---|---|---|
| Mean Retroreflectivity (cd/lx/m²) | 29 | 187 |
| Retroreflectivity Std Dev | 18 | 89.9 |
| Retroreflectivity RSD (%) | 63 | 48 |
| Daytime Mean Detection Rate | 0.80 | 0.88 |
| Daytime Detection Std Dev | 0.17 | 0.06 |
| Daytime Detection RSD (%) | 21 | 6 |
| Nighttime Mean Detection Rate | 0.83 | 0.87 |
| Nighttime Detection Std Dev | 0.19 | 0.08 |
| Nighttime Detection RSD (%) | 23 | 9 |
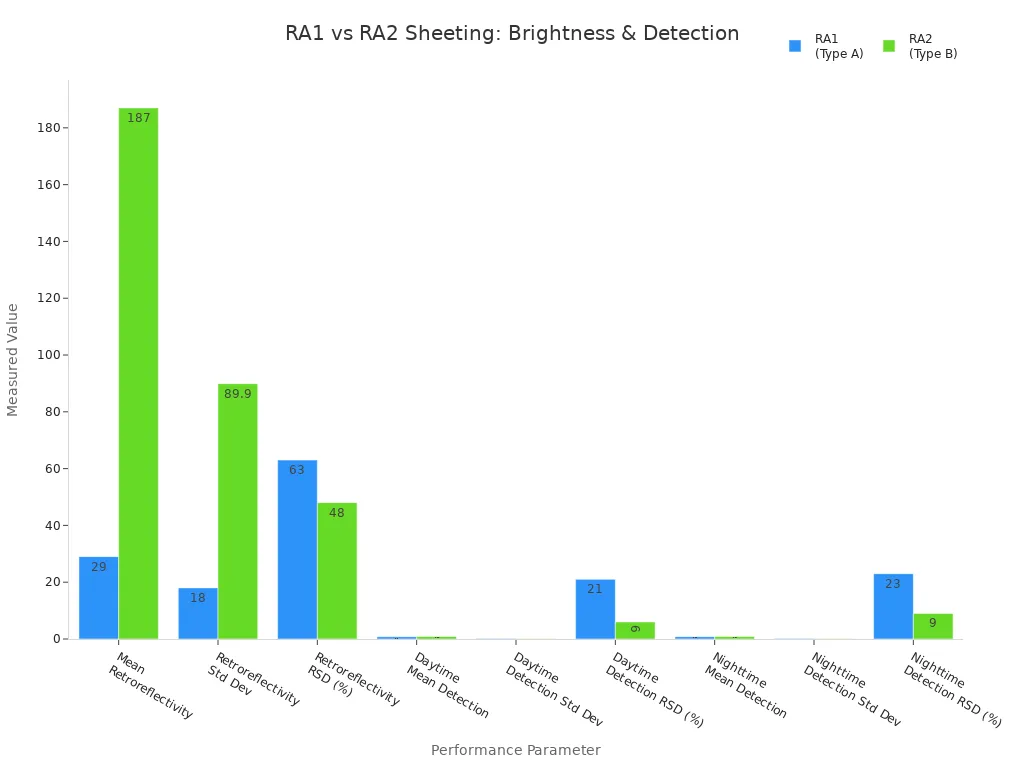
RA2 reflective is much brighter than RA1 and helps drivers see signs better. The chart shows RA2 reflective is easier to spot, especially at night. RA2 reflective also works the same way every time, with less change in how well it can be seen.
RA2 reflective is used for warning signs, speed limits, and rules on main roads. Its prismatic design, like 3M’s High Intensity Prismatic Grade, meets EN 12899-1:2007 Class RA2 rules. As a result, it lasts a long time and is easy to see at night. Furthermore, RA2 reflective enhances road safety by making signs clear in all types of light.
Tip: Class ra2 is best for roads without lights and is needed for motorways and dual carriageways, unless there are street lights.
R3B Reflective Overview
R3B reflective, or ra3 reflective, is a top-quality reflective sheeting. It uses special microprisms with cut-off tops to reflect lots of light. R3B reflective is brighter than both RA1 and RA2 reflective. It is made for signs that must be seen very clearly.
| Specification Aspect | R3B Reflective Sheeting (UK Standard) | Notes/Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Material Technology | Improved micro prismatic technology using traditional truncated prisms | More advanced than RA1 and RA2; less advanced than R3C full cube micro prismatic technology |
| Reflectivity / Light Return | Superior light return compared to RA1 and RA2 classes | Provides enhanced conspicuity for permanent traffic signs |
| Performance Benchmark | Enhanced reflectivity suitable for permanent traffic signs requiring better visibility than standard | Positioned below R3C which offers highest reflectivity |
| Construction | Traditional truncated prisms | R3C uses full cube prisms for maximum reflection |
| Durability and Warranty | CE marked; warranties up to 15 years ensuring durability and sustained retroreflective performance | Warranty period longer than RA1 and RA2 classes |
| UK Standards Reference | Defined in UK National Annex to BS EN 12899-1:2007 | Specifies R3B as premium grade prismatic sheeting for higher performance needs than RA2 |
| Application | Used where higher performance than RA2 is needed but not as high as R3C | Suitable for permanent traffic signs requiring improved visibility |
R3B reflective is needed for fast and risky roads. Motorways and big country roads use ra3 reflective to keep signs bright day and night. The UK Traffic Signs Manual and TSRGD 2016 say r3b reflective is important for these places. R3B reflective helps keep drivers safe when they are going fast.
- R3B reflective has longer warranties, sometimes up to 15 years.
- It uses microprisms to make signs very bright.
- Ra3 reflective is needed for motorway signs, overhead signs, and dangerous junctions.
- This material keeps signs easy to see in all weather and light.
Note: R3B reflective is best for permanent signs on fast roads, where being seen and lasting a long time matter most.
Performance and Applications
Reflectivity and Durability
Reflectivity and durability are very important for UK road signs. RA1 reflective sheeting gives basic brightness. It is good for signs in quiet places where cars go slow. RA2 reflective sheeting is much brighter than RA1. It helps drivers see signs from farther away, even in bad weather. RA2 reflective is used on most main roads and busy streets. RA3 reflective, also called R3B, is the brightest type. It is used for signs on motorways and fast roads.
How long each type lasts depends on its material and where it is put. The table below shows how long each type usually lasts and where it is used:
| Reflective Sheeting Type | Average Lifespan (years) | Durability Level | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| RA1 reflective | 5 to 7 | Adequate | Urban, residential, low-traffic roads |
| RA2 reflective | 7 to 10 | More durable | Main roads, busier streets |
| RA3 reflective | 10+ | Highest | Motorways, highways, critical areas |
Weather and sunlight can change how long reflective traffic signs last. Getting old is the main reason signs lose their brightness. Wet or sunny places can make signs fade faster. Checking signs often helps keep them safe and easy to see.
Tip: Picking the right reflective sheeting keeps road signs bright and clear for a long time.
Applications by Road Type
Different roads require different levels of brightness. RA1 reflective works best for signs on quiet streets and private roads, where bright signs are not necessary. The most common reflective sheeting for signs on main roads and busy areas is RA2, which enhances visibility for drivers at night. RA2 reflective sheeting also suits warning signs and speed limits. For motorways and fast roads, RA3 reflective sheeting is typically used. It provides the brightest reflection and has the longest lifespan.
Bright road signs help drivers react fast and stay safe. The right reflective sheeting keeps reflective traffic signs working well in rain, fog, or strong sunlight.
Choosing the Right Reflective Standard

Compliance and Regulations
Picking the right reflective sheeting for UK road signs is not just a choice; it is required by law. These rules ensure that every sign is easy to see and safe. Therefore, councils and builders must follow these regulations to keep roads safe and avoid getting into trouble.
Key things to remember for following the rules are:
- Reflective sheeting must meet British standards like bs 8442 for good quality.
- CE marking is needed. This mark shows the material is safe and meets reflectivity rules.
- All reflective materials must be checked before being put up. Councils look at each sign to make sure it meets the rules.
- Signs must be checked often and kept in good shape. They need to stay bright and easy to see.
| Reflective Sheeting Class | Minimum Reflectivity (cd/m²/lux) | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| RA1 | 75 | Motorway and primary route signs needing high visibility |
| RA2 | 30 | Secondary and local roads with lower visibility needs |
Cost and Performance Balance
Finding the right balance between cost and performance is important. Some people think using cheaper materials saves money. But this can make roads less safe and cost more later. Reflectivity rules help buyers pick the best sheeting for each road.
People sometimes mix up grades or forget the rules. For example, using Engineer Grade on a busy road instead of a better grade makes signs harder to see. This can cause more crashes, fines, or delays. It also means signs may need to be replaced sooner, costing more in the end.
A smart plan considers both the price and how long the material lasts. While RA1 sheeting costs less, it is only suitable for quiet roads. On the other hand, RA2 and R3B last longer and are brighter, making them better for main roads and motorways. Ultimately, picking the right grade ensures signs remain bright and comply with regulations.
Reflectivity rules protect drivers and councils. They make sure every sign fits its place and works for years.
The table below shows how RA1, RA2, and R3B are different:
| Factor | RA1 | RA2 | R3B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reflectivity | Lowest | Moderate | Highest |
| Lifespan | 7 years | 10–12 years | 12–15 years |
| Best Use | Local roads | Urban roads | Highways |
Picking the right standard for each road helps drivers see reflective traffic signs better. Additionally, it helps them follow the rules. Councils should make sure traffic signs are the right size for the speed. Furthermore, they should use clear writing and choose the best reflectivity for each place. For tricky projects, they should check official advice or ask experts. In doing so, they ensure road safety for everyone.
FAQ
What does “retroreflective” mean for traffic signs?
Retroreflective means the sign bounces light from car headlights back towards the driver. This makes the sign easy to see at night or in poor weather. Drivers can spot important information quickly.
Why do some signs look brighter than others?
Some signs use higher-grade reflective sheeting, like RA2 or R3B. These materials reflect more light. Signs on busy or fast roads need to be brighter for safety.
How often should councils check traffic signs for reflectivity?
Councils should check signs every few years. They look for fading or damage. Regular checks help keep signs bright and easy to see.
Can old signs be upgraded to a higher reflective standard?
Yes, councils can replace old signs with new ones using better reflective sheeting. Upgrading helps improve visibility and road safety.
Who decides which reflective standard to use for each road?
The Department for Transport sets the rules. Councils follow these rules when choosing reflective sheeting. They pick the right standard based on road type and speed.