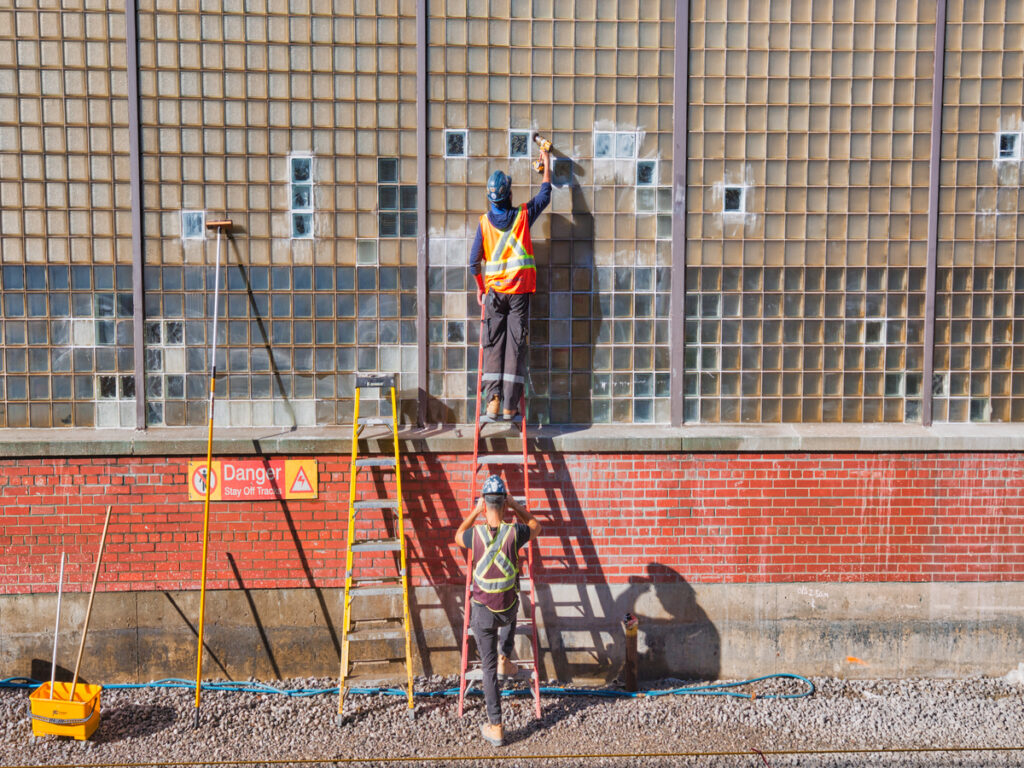
Garantindo Conformidade com OSHA é uma prioridade máxima ao instalar cabeços de construção em qualquer zona de trabalho ativa. O não cumprimento pode causar acidentes, multas, ou atrasos no projeto. Postes de amarração de construção devidamente instalados protegem os trabalhadores, pedestres, e equipamentos contra intrusão de veículos. Listas de verificação de segurança e procedimentos claros ajudam as equipes a evitar erros. Cada local de trabalho se beneficia quando as equipes seguem os padrões de segurança estabelecidos.
OPTRAFFIC oferece orientação especializada e durável Bollards de tráfego para venda que ajudam a garantir que seu site esteja em conformidade com os regulamentos da OSHA, protegendo tanto os trabalhadores como a propriedade. Com suas soluções confiáveis de postes de amarração, seu site pode permanecer seguro e compatível, minimizando riscos enquanto otimiza a segurança.
Takeaways -chave
- A instalação adequada de cabeços de construção protege os trabalhadores e os equipamentos, evitando invasões de veículos e reduzindo acidentes..
- Seguindo os padrões e diretrizes de segurança da OSHA, incluindo espaçamento e posicionamento correto do poste de amarração, ajuda a evitar multas e mantém os locais de trabalho seguros.
- A escolha do tipo e material de poste de amarração corretos depende das necessidades do local, riscos de impacto, e custos de manutenção para garantir proteção duradoura.
- Inspeções e manutenção regulares mantêm os cabeços eficazes e em conformidade, prevenir danos e garantir a segurança do trabalhador.
- O uso de listas de verificação e aconselhamento especializado melhora a qualidade da instalação e ajuda as equipes a atender aos requisitos da OSHA com confiança.
OSHA e segurança na construção
O que é OSHA?
O Administração de Segurança e Saúde Ocupacional (OSHA) define e aplica padrões de segurança para locais de trabalho nos Estados Unidos. OSHA começou em 1970 para lidar com as altas taxas de lesões e mortes no local de trabalho. Desde então, A OSHA desempenhou um papel importante na melhoria da segurança dos trabalhadores da construção. A tabela a seguir mostra como os esforços da OSHA reduziram lesões e mortes ao longo do tempo:
| Descrição da métrica | Dados Numéricos | Ano(é) |
|---|---|---|
| Média de mortes de trabalhadores por dia | 38 | 1970 |
| Média de mortes de trabalhadores por dia | 15 | 2022 |
| Taxa de lesões e doenças por 100 trabalhadores | 10.9 | 1972 |
| Taxa de lesões e doenças por 100 trabalhadores | 2.7 | 2022 |
| Taxa de mortalidade por 100,000 funcionários | 3.7 | 2022 |
| Porcentagem de inspeções de segurança da OSHA em canteiros de obras | Aproximadamente 50% | 2022 |
| Número de violações da proteção contra quedas | 5,465 | 2021 |
| Total de multas por violações de proteção contra quedas | $28.8 milhão | 2021 |
O papel da OSHA nas zonas de construção
A OSHA se concentra em zonas de construção porque esses locais apresentam muitos perigos. Inspetores visitam quase metade de todos os canteiros de obras todos os anos. OSHA impõe regras que protegem os trabalhadores contra quedas, acidentes com equipamentos, e invasões de veículos. A agência usa multas e penalidades para garantir que as empresas sigam os padrões de segurança. Por exemplo, um único empreiteiro já enfrentou uma penalidade de $8.35 milhões por violações. As citações mais comuns envolvem proteção contra quedas, escadas, e andaimes. Esses esforços ajudam a reduzir o número de feridos e mortes nos canteiros de obras.
| Métrica | Estatística | Explicação |
|---|---|---|
| Penalidade máxima da OSHA para um único contratante | $8.35 milhão (2010) | Demonstra o poder de aplicação da OSHA através de sanções financeiras |
| Penalidade da OSHA por violação grave | Até $16,550 | Mostra consequências financeiras para violações de segurança |
| Penalidade da OSHA por dia por não redução | $16,550 | Destaca penalidades contínuas por não conformidade |
| Penalidade da OSHA por violação intencional/repetida | Até $165,514 | Enfatiza a gravidade das violações repetidas |
| Regulamento de construção OSHA mais citado (2023) | Falta de proteção contra quedas: 6,616 citações | Indica a área de foco da aplicação da OSHA na segurança da construção |
| Mortes em construção anualmente | Sobre 1,000 desde 2016 | Contextualiza o custo humano que a OSHA pretende reduzir |
| Porcentagem de fatalidades causadas pelos perigos do “Foco Quatro” (2011-2020) | 65% de ferimentos fatais | Mostra o foco da OSHA nas principais categorias de perigo na construção |
Por que a instalação do poste de amarração é importante
Os cabeços de construção desempenham um papel fundamental na segurança do local. Eles impedem que os veículos entrem em áreas restritas e protegem os trabalhadores, pedestres, e equipamento. Cada dia, postes de amarração impedem até 100 veículo bate em prédios, que ajuda a evitar milhares de feridos e mortes todos os anos. Os postes de amarração criam barreiras fortes que reduzem acidentes e melhoram o fluxo do tráfego. Projetos do mundo real, como o Public Square Bollard Project em Cleveland, mostram como a substituição de barreiras temporárias por postes de amarração removíveis aumenta a segurança para todos no local. Colocação adequada nos portões de acesso, passarelas, e os perímetros do local controlam o tráfego e mantêm veículos não autorizados afastados. Usar o método e o material de instalação corretos garante que os cabeços atendam aos rigorosos padrões de segurança e forneçam proteção duradoura.
Principais regulamentos da OSHA

Padrões de controle de tráfego
OSHA exige controle de tráfego claro em zonas de construção para proteger os trabalhadores e o público. Esses padrões incluem o uso de sinais, barreiras, e postes de amarração para guiar veículos e prevenir acidentes. O Manual sobre Dispositivos Uniformes de Controle de Tráfego (MUTCD) trabalha em conjunto com as regras da OSHA para definir diretrizes para sinais e barreiras. Os canteiros de obras devem usar postes de amarração visíveis e resistentes para bloquear veículos não autorizados. O controle de tráfego adequado reduz a confusão e mantém todos seguros.
Requisitos de segurança do trabalhador
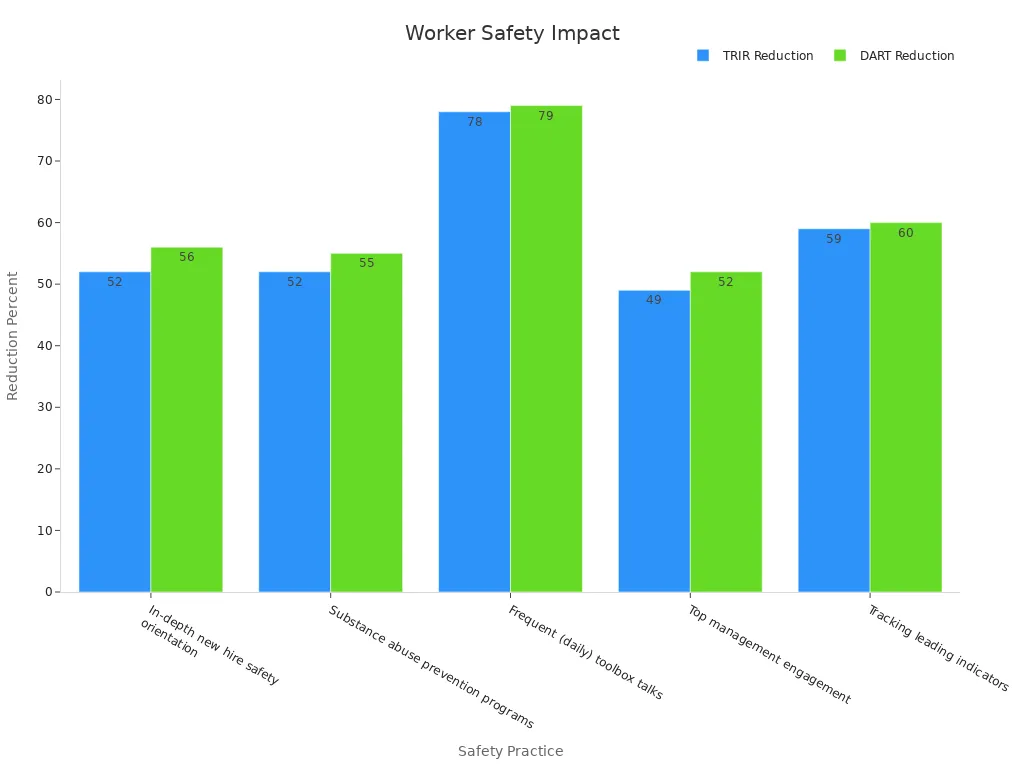
Os requisitos de segurança do trabalhador constituem a espinha dorsal da missão da OSHA. Os empregadores devem treinar os trabalhadores, fornecer equipamentos de segurança, e compartilhar informações sobre perigos. Pesquisas mostram que fortes práticas de segurança levam a menos incidentes. Por exemplo, conversas frequentes sobre segurança e envolvimento da gestão podem reduzir as taxas de incidentes em mais de 50%. A tabela abaixo destaca como práticas de segurança específicas reduzem lesões no local de trabalho:
| Prática de Segurança | Redução no TRIR | Redução no DART |
|---|---|---|
| Orientação detalhada sobre segurança para novos contratados | 52% | 56% |
| Programas de prevenção do abuso de substâncias | 52% | 55% |
| Freqüente (diário) palestras de segurança | 78% | 79% |
| Engajamento da alta administração | 49% | 52% |
| Acompanhamento de indicadores antecedentes | 59% | 60% |
Cláusula de Dever Geral
A Cláusula de Dever Geral exige que os empregadores mantenham os locais de trabalho livres de perigos reconhecidos. Esta regra cobre perigos não abordados por padrões específicos da OSHA. Seguindo esta cláusula, empresas melhoram a cultura de segurança e reduzem acidentes. Os dados mostram que a OSHA usa a Cláusula de Dever Geral por cerca de 1.5% de citações, tornando-o uma ferramenta fundamental para perigos não regulamentados. Os empregadores que seguem esta regra apresentam menos lesões, custos mais baixos, e melhor moral.
Observação: O Cláusula de Dever Geral dá à OSHA a flexibilidade para lidar com perigos novos ou únicos, garantindo que todos os riscos recebam atenção.
Outras normas relevantes
Outras normas da OSHA também ajudam a manter os locais de construção seguros. Estudos mostram que as inspeções e a fiscalização da OSHA reduzem as taxas e custos de lesões. Por exemplo, após inspeções com penalidades, as taxas de lesões caem em até 24%. Esses padrões cobrem tópicos como montagem de aço, segurança elétrica, e equipamentos de proteção individual. Seguindo todas as regras relevantes, equipes de construção criam ambientes mais seguros e evitam acidentes dispendiosos.
Postes de amarração para construção: Tipos e usos

Bollards fixos e removíveis
Os canteiros de obras usam postes de amarração fixos e removíveis para controlar o acesso e proteger os trabalhadores. Os postes de amarração fixos permanecem no lugar e proporcionam resistência, Barreiras permanentes. Os postes de amarração removíveis oferecem flexibilidade para alterar as necessidades do local. A tabela abaixo compara seu desempenho em zonas de construção:
| Métrica de desempenho | Boldes fixos | Boldes removíveis |
|---|---|---|
| Resistência ao impacto | Alto; revestimento de concreto profundo | Moderado; não profundamente ancorado |
| Método de instalação | Permanente, requer trabalho de base | Rápido, usa mangas de aterramento ou placas de base |
| Flexibilidade | Sem adaptabilidade após a instalação | Pode ser movido ou armazenado conforme necessário |
| Manutenção | Mínimo após a instalação | Mais frequente, especialmente para peças móveis |
| Custo | Maior adiantamento, menor a longo prazo | Menor adiantamento, maior em andamento |
| Casos de uso adequados | Alta segurança, proteção permanente | Zonas temporárias, mudanças nas necessidades de acesso |
Opções de material
A escolha do material afeta a durabilidade, manutenção, e custo. O aço e o concreto oferecem forte resistência ao impacto, mas podem precisar de mais manutenção. Polímero e aço inoxidável proporcionam alta durabilidade e baixa manutenção. A tabela abaixo descreve as principais diferenças:
| Material | Custo inicial | Manutenção | Durabilidade e Substituição | Notas |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aço | Mais baixo | Precisa de repintura | Comprometido após impactos | Propenso a enferrujar |
| Concreto | Moderado | Precisa de repintura | Suporta força, caro para substituir | As fundações podem precisar de reparos |
| Polímero | Mais alto | Mínimo | Suporta múltiplos impactos | UV estável, sem ferrugem, fácil de limpar |
| Aço inoxidável | Mais alto | Mínimo | Altamente durável, resistente à ferrugem | Ideal para condições climáticas adversas e tráfego intenso |
Avaliações de falhas
As classificações de colisão ajudam as equipes a selecionar os cabeços de construção certos para segurança. Padrões como classificações DOS K, ASTM F2656-07, e BSI PAS 68:2010 medir quão bem os postes de amarração param os veículos. Por exemplo, uma classificação K4 significa que um poste de amarração pode parar um caminhão de 15.000 libras em 30 MPH com menos de 1 metro de penetração. ASTM F2656-07 usa classificações como M30 P1, o que significa um caminhão médio em 30 MPH com menos de 1 metro de penetração. Essas classificações garantem que os cabeços atendam à OSHA e Padrões de segurança MUTCD.
Quando usar cada tipo
Os cabeços fixos funcionam melhor em zonas de alta segurança ou de construção permanente. Os postes de amarração removíveis cabem em áreas onde o acesso muda frequentemente, como zonas de trabalho temporárias ou espaços para eventos. Os cabeços de polímero são adequados para áreas de alto tráfego que necessitam de visibilidade e baixa manutenção. Os postes de amarração em aço inoxidável resistem à ferrugem e duram em condições climáticas adversas. As equipes devem sempre verificar a OSHA, MUTCD, e diretrizes da ADA antes de escolher e colocar cabeços de construção.
Dica: Sempre combine o tipo e o material do poste de amarração com as necessidades de segurança do local e as velocidades esperadas de impacto do veículo.
Colocação e espaçamento
Prevenindo a Intrusão de Veículos
A colocação estratégica de cabeços de construção cria uma forte barreira entre veículos e zonas de trabalho. Cada ano, incursões de veículos em vitrines ferem milhares de pessoas e causam muitas mortes. Uma pesquisa do Storefront Safety Council mostra que 90% desses incidentes resultam de erro do motorista ou falha mecânica. Instalar postes de amarração nos locais certos pode evitar esses acidentes. Depois que cidades como Nova York e Londres adicionaram postes de amarração com classificação de colisão, eles viram menos invasões de veículos em áreas lotadas. Esses cabeços absorvem o impacto e impedem a entrada de veículos não autorizados em zonas restritas. Os gerentes do site devem sempre avaliar os padrões de tráfego, terreno, e necessidades de segurança antes de decidir onde instalar barreiras.
Zonas Seguras para Trabalhadores
As zonas seguras protegem os trabalhadores da movimentação de veículos e equipamentos. As equipes usam postes de construção para marcar os limites dessas zonas. Os trabalhadores ficam mais seguros quando barreiras os separam das faixas de tráfego ativas. Colocação de postes de amarração nas entradas do local, passarelas, e ao redor das áreas de armazenamento de equipamentos ajuda a criar, espaços protegidos. Esta configuração reduz o risco de entrada acidental de veículos e mantém os trabalhadores concentrados nas suas tarefas.
Dica: Sempre use postes de amarração de alta visibilidade ou adicione fita reflexiva para aumentar a conscientização, especialmente em condições de pouca luz.
Espaçamento e Alinhamento
O espaçamento e o alinhamento adequados garantem que os cabeços bloqueiem os veículos sem criar perigos para os pedestres. OSHA e MUTCD recomendam colocar postes de amarração próximos o suficiente para impedir a passagem de carros, mas distantes o suficiente para acesso de emergência. Uma diretriz comum é 3 para 5 pés entre postes. O alinhamento dos cabeços em linha reta melhora a aparência e a eficácia. As equipes devem verificar os códigos locais para quaisquer requisitos especiais de espaçamento.
Fluxo de tráfego e segregação
Postes de amarração bem posicionados ajudam a gerenciar o fluxo de tráfego e a manter veículos e pedestres separados. Estudos mostram que o uso de folhas fluorescentes laranja em sinais de alerta e a colocação de sinais de mensagens mutáveis (Cms) em distâncias específicas melhora as mudanças de faixa e reduz os conflitos de trânsito. A tabela abaixo destaca as principais medidas que melhoram o fluxo e a segregação do tráfego:
| Medição | Efeito no fluxo de tráfego e na segregação | Validação Estatística |
|---|---|---|
| Folhas laranja fluorescentes em placas | Menos conflitos de trânsito, mais caminhões saem da faixa da esquerda mais cedo | Redução significativa de conflitos e ocupação de faixa |
| CMS em 3,960 pés de avanço, painel de seta em 2,000 ft | Mudanças de faixa mais suaves, menos saídas tardias | Apoiado por dados em grande escala |
Postes de amarração para construção, quando combinado com essas estratégias, criar zonas de construção mais seguras e organizadas.
Altura, Material, e durabilidade
Requisitos de altura e tamanho
A altura do poste de amarração desempenha um papel crítico tanto na visibilidade quanto na eficácia. A maioria dos cabeços de construção ficam entre 36 e 48 polegadas de altura. Esta faixa garante que motoristas e pedestres possam ver claramente as barreiras. Os padrões da indústria recomendam esta altura para equilibrar segurança e acessibilidade. O espaçamento entre os postes de amarração não deve exceder 48 polegadas. Isso evita a passagem de veículos e permite que as pessoas se movimentem livremente. Estas diretrizes refletem as melhores práticas encontradas em dados de testes de colisão e códigos de segurança.
- Altura típica: 36–48 polegadas
- Espaçamento máximo: 48 polegadas
- Garante visibilidade e acessibilidade
Resistência Material
Zonas de construção exigem cabeços de alta resistência. A maioria dos locais utiliza tubos de ferro fundido ou aço ancorados em concreto. Esses materiais oferecem forte resistência aos impactos do veículo. Laboratórios credenciados, certificado pela ISO/IEC 17025, postes de teste para resistência à tração, resistência à compressão, e resistência ao esmagamento. Esses testes confirmam que os cabeços podem suportar as forças esperadas em colisões no mundo real. Normas como ASTM F2656, NÃO 68, e iwa 14 definir benchmarks para resistência a colisões. Por exemplo, uma classificação M50 significa que um poste de amarração pode parar um veículo de 15.000 libras viajando a 50 km/h.
Durabilidade em áreas de alto tráfego
A durabilidade torna-se essencial em zonas de construção movimentadas. Os cabeços de aço e concreto oferecem desempenho de longo prazo e resistem a impactos repetidos. Postes de amarração de plástico, embora menos durável, fornecem flexibilidade e são fáceis de instalar. Eles funcionam bem em áreas temporárias ou de baixo impacto. O aço inoxidável resiste à ferrugem e às intempéries, tornando -o adequado para uso ao ar livre. Inspeções regulares ajudam a manter a durabilidade e garantem proteção contínua.
Selecionando o material certo
Escolher o material certo envolve equilibrar custos, durabilidade, e manutenção. Os postes de amarração de plástico custam menos e exigem manutenção mínima, tornando-os ideais para projetos de curto prazo. Aço e concreto oferecem maior resistência para áreas de alto risco. Mais de cinco anos, usar coberturas plásticas em vez de pintar postes de aço pode economizar até $464,000 para 3,200 Postagens. O custo inicial por postagem é semelhante, mas as tampas de plástico eliminam despesas contínuas de manutenção. Esta análise de custo-benefício ajuda os gerentes de projeto a selecionar materiais que atendam às necessidades de segurança e de orçamento.
| Ano | Custo de pintura (3,200 Postagens) | Custo de coberturas de poste de amarração de plástico | Poupança Anual (Pintura vs.. Capas) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primeiro ano | $112,000 | $96,000 | $16,000 |
| Segundo ano | $112,000 | $0 | $112,000 |
| Terceiro ano | $112,000 | $0 | $112,000 |
| Quarto ano | $112,000 | $0 | $112,000 |
| Quinto ano | $112,000 | $0 | $112,000 |
Dica: Os gerentes de projeto devem considerar tanto o investimento inicial quanto a manutenção a longo prazo ao selecionar materiais de amarração para zonas de construção.
Métodos de instalação
No solo vs.. Montagem em superfície
Escolhendo o direito método de instalação para postes de construção depende das necessidades do local e dos requisitos de segurança. No solo (integrado) os cabeços oferecem o mais alto nível de estabilidade e resistência ao impacto. As equipes instalam esses cabeços em uma fundação de concreto abaixo do solo. Os postes de amarração montados na superfície são fixados ao concreto ou asfalto existente usando parafusos resistentes. Este método funciona bem quando não é possível escavar ou quando é necessária uma instalação rápida.
| Tipo de instalação | Nível de estabilidade | Método de instalação | Aplicações adequadas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Integrado (No solo) | Máxima estabilidade e resistência ao impacto | Instalado em uma fundação de concreto subterrânea | Áreas de alta segurança e tráfego intenso |
| Montado em superfície | Menos estabilidade do que incorporado | Ancorado em concreto ou asfalto com parafusos resistentes | Quando a escavação não for possível ou proibida; instalação mais rápida |
Os gerentes de projeto devem selecionar o tipo de instalação com base no nível de proteção exigido e nas condições do local.
Etapas de instalação
A instalação adequada garante que os cabeços de construção forneçam proteção confiável. As equipes devem seguir estas etapas para conformidade com OSHA e MUTCD:
- Planeje o layout
Marque os locais exatos para cada poste de amarração. Use desenhos do local e mapas de fluxo de tráfego para orientar o posicionamento. - Prepare o local
Para postes de amarração enterrados, cavar buracos na profundidade e largura necessárias. Para postes de montagem em superfície, limpe e nivele a superfície. - Verifique se há utilitários
Sempre verifique se há utilidades subterrâneas antes de cavar. Esta etapa evita acidentes e reparos dispendiosos. - Instale o poste de amarração
- Para no solo: Coloque o poste de amarração no buraco e preencha com concreto. Certifique-se de que o poste de amarração esteja reto e na altura correta.
- Para montagem em superfície: Posicione o poste de amarração e fixe-o com chumbadores resistentes.
- Permitir a cura
Deixe o concreto curar completamente antes de expor o poste de amarração ao impacto ou uso pesado. - Inspecionar e Documentar
Inspecione cada poste de amarração quanto ao alinhamento e estabilidade. Registre os detalhes da instalação para conformidade e manutenção futura.
Dica: Sempre siga as instruções do fabricante e os códigos locais quanto à profundidade de instalação, tamanho do parafuso, e tempo de cura.
Protegendo os postes de amarração
Proteger adequadamente os cabeços de construção é essencial para segurança e acesso de emergência. Existem vários métodos, cada um com benefícios exclusivos:
- Os postes de amarração dobráveis com cadeado levam cerca de 30 a 35 segundos para recolher três unidades usando uma caixa de chaves e um cadeado. Ferrugem ou detritos às vezes podem causar problemas de bloqueio.
- Os postes de amarração dobráveis da chave hidrante desbloqueiam e desmoronam em cerca de 20 segundos para três unidades. Os socorristas geralmente carregam a chave inglesa necessária.
- Os cabeços de força do aparelho desmoronam aproximadamente 5 segundos quando atingido por um pára-choque de veículo de emergência. Esses postes de amarração são projetados para reparo rápido após o uso.
Essas opções ajudam a equilibrar segurança com acesso de emergência. Estudos da FEMA mostram que os cabeços continuam sendo uma medida de segurança econômica e versátil para muitos locais.
Observação: Sempre teste mecanismos de travamento e peças móveis durante inspeções de rotina para garantir uma operação confiável.
Avaliação do local
Uma avaliação completa do local constitui a base de uma instalação de poste de amarração segura e eficaz. Estudos de desenvolvimento urbano mostram que cidades como Londres reduziram os ataques de veículos em zonas pedonais em 30% depois de instalar postes de amarração retráteis com planejamento cuidadoso. As equipes devem avaliar os padrões de tráfego, movimento de pedestres, condições do solo, e a presença de utilidades subterrâneas. A verificação de utilidades evita perigos e evita reparos caros. A avaliação correta ajuda a determinar o melhor tipo de poste de amarração, colocação, e método de instalação para cada local.
Chamar: Avaliações abrangentes do local melhoram a segurança, durabilidade, e a eficácia a longo prazo dos cabeços de construção.
Manutenção e inspeção
Inspeções regulares
Inspeções regulares ajudam a manter os cabeços de construção eficazes e seguros. As equipes devem verificar se há danos visíveis, acessórios soltos, e sinais de ferrugem ou corrosão. Embora alguns acreditem que inspeções mais frequentes reduzem os acidentes, pesquisa de Miscetti et al. (2008) não encontraram evidências claras de que o aumento dos intervalos de inspeção leve a menos lesões nos canteiros de obras. Em vez de, o foco deve permanecer no rigor e na documentação adequada. Os inspetores devem usar uma lista de verificação para registrar as descobertas e anotar quaisquer reparos necessários. Manter registros detalhados apoia a conformidade com a OSHA e ajuda a monitorar a condição de cada poste de amarração ao longo do tempo.
Manutenção contínua
A manutenção contínua garante que os cabeços de construção continuem a proteger os trabalhadores e os equipamentos. As equipes devem limpar os cabeços regularmente com água morna e sabão para remover sujeira e detritos. Esta etapa simples evita acúmulos que podem afetar o desempenho. Lubrificação de peças móveis, como dobradiças em postes de amarração removíveis, os mantém funcionando sem problemas. Seguir as diretrizes do fabricante para lubrificação e limpeza ajuda a evitar desgaste desnecessário. No inverno, a aplicação de agentes descongelantes e a remoção da neve evitam falhas operacionais.
Avaliando e substituindo postes de amarração
A avaliação envolve a verificação de cada poste de amarração em busca de rachaduras, dentes, ou outros sinais de danos. Se um poste de amarração apresentar desgaste severo ou não puder ser reparado, a substituição se torna necessária. As equipes devem procurar por ferrugem, âncoras soltas, ou postes dobrados. Quando o dano é encontrado, ação imediata reduz o risco de acidentes. Os serviços de manutenção profissionais podem fornecer inspeções especializadas e reparos oportunos, que prolongam a vida útil dos cabeços de construção.
Melhores práticas de manutenção
As melhores práticas para manutenção incluem inspeções mensais, limpeza regular, e reparos oportunos. A tabela abaixo resume as principais ações de manutenção para ambientes de alto impacto:
| Tarefa de manutenção | Freqüência | Propósito |
|---|---|---|
| Inspeção visual | Mensal | Detectar rachaduras, ferrugem, ou desgaste |
| Limpeza | Mensal | Remova sujeira e detritos |
| Lubrificação | Como recomendado | Garanta um funcionamento suave |
| Cuidados de inverno | Conforme necessário | Evite congelamentos e falhas |
| Inspeção profissional | Anualmente | Avaliação especializada e reparos |
Dica: Rotinas de manutenção consistentes ajudam os cabeços de construção a durar mais e a ter melhor desempenho em condições exigentes.
Violações e soluções comuns
Espaçamento inadequado
Muitos canteiros de obras cometem o erro de colocar postes de amarração muito distantes uns dos outros. Grandes lacunas permitem que os veículos passem, que coloca trabalhadores e pedestres em risco. OSHA e MUTCD recomendam um espaçamento máximo de 48 centímetros entre os postes de amarração. As equipes devem medir a distância entre cada unidade antes de finalizar a instalação. Usar uma lista de verificação de espaçamento ajuda a evitar esse erro comum.
Dica: Sempre verifique o espaçamento com uma fita métrica antes de fixar cada poste de amarração.
Colocação inadequada
A colocação inadequada geralmente leva a condições inseguras. Algumas equipes instalam cabeços de construção em passarelas de pedestres ou bloqueiam saídas de emergência. Este erro pode criar novos perigos em vez de os prevenir. Os gerentes do local devem revisar os planos do local e os mapas de fluxo de tráfego antes da instalação. Colocação de postes de amarração em pontos de acesso, perímetros, e ao redor das zonas de equipamentos mantém todos seguros.
Tabela de erros comuns de posicionamento
| Tipo de erro | Impacto | Solução |
|---|---|---|
| Bloqueando passarelas | Viagens, acesso bloqueado | Siga as diretrizes da ADA |
| Perto das saídas | Saída de emergência bloqueada | Mantenha as saídas desobstruídas |
| Alinhamento aleatório | Confusão, segurança reduzida | Use planos de layout do site |
Postes de amarração inseguros
Postes de amarração inseguros não fornecem proteção real. Se um poste de amarração estiver solto ou não ancorado corretamente, ele pode se mover durante o impacto. Workers should always check that each unit is firmly attached to its base. Regular inspections help catch loose fittings early. Teams should follow manufacturer instructions for anchoring and test stability after installation.
Incorrect Materials
Using the wrong materials reduces the effectiveness of construction bollards. Some sites use plastic units in high-impact areas where steel or concrete is needed. This choice can lead to quick damage or failure during a crash. Project managers should select materials based on expected vehicle speeds and site risks. Reviewing crash ratings and material strength data ensures the right choice for each location.
Observação: Choosing the correct material and installation method increases safety and reduces long-term costs.
Garantindo conformidade
OSHA Guidelines Summary
OSHA fornece regras claras para segurança em zonas de construção. Estas diretrizes cobrem o uso de barreiras, Sinais, e postes de construção. OSHA espera que os empregadores sigam a cláusula de dever geral, o que significa que eles devem manter o local de trabalho livre de perigos conhecidos. O manual em dispositivos uniformes de controle de tráfego (MUTCD) suporta OSHA, fornecendo detalhes extras sobre controle de tráfego. Junto, essas regras ajudam as equipes a criar ambientes de trabalho mais seguros.
Dica: Sempre revise as atualizações mais recentes da OSHA e MUTCD antes de iniciar um novo projeto.
Importância da conformidade
A conformidade com os padrões OSHA protege os trabalhadores, pedestres, e propriedade. Quando as equipes seguem as regras, eles reduzem o risco de acidentes e lesões. A conformidade com a OSHA também ajuda as empresas a evitar multas dispendiosas e atrasos em projetos. Os registros de segurança melhoram quando as equipes usam barreiras adequadas e seguem as melhores práticas. Uma boa conformidade demonstra um compromisso com a segurança e constrói a confiança dos clientes e do público.
Atendendo aos requisitos
As equipes podem atender aos requisitos da OSHA seguindo algumas etapas principais:
- Treinar todos os trabalhadores sobre procedimentos de segurança e conscientização sobre perigos.
- Use postes de amarração e outras barreiras nos locais certos.
- Inspecione e mantenha todos os equipamentos de segurança regularmente.
- Mantenha registros detalhados de inspeções e reparos.
- Revise os planos do local e atualize-os conforme necessário.
Uma lista de verificação ajuda as equipes a se manterem organizadas e garante que nada seja esquecido.
Assistência especializada
Às vezes, projetos precisam de aconselhamento especializado. Consultores de segurança e especialistas da OSHA podem revisar os planos do local e sugerir melhorias. Eles ajudam as equipes a compreender regras complexas e evitar erros comuns. Muitas empresas oferecem sessões de treinamento e avaliações locais. Esses serviços ajudam a garantir que cada instalação atenda aos padrões da OSHA e mantenha todos seguros.
Observação: Buscar ajuda especializada no início do projeto pode evitar erros dispendiosos e melhorar a segurança geral.
A conformidade com a OSHA continua essencial para a instalação segura de postes de amarração na construção. As equipes melhoram a segurança do local concentrando-se no posicionamento adequado, instalação segura, e manutenção regular. O uso de listas de verificação ajuda as equipes a evitar erros comuns. Projetos complexos beneficiam-se de orientação especializada.
Manter-se atualizado com os padrões da OSHA protege os trabalhadores e o público. Treinamento contínuo e revisões regulares das regras de segurança mantêm todos os locais de trabalho seguros.
Os leitores devem priorizar a segurança e tornar a conformidade uma parte rotineira de cada projeto.
Perguntas frequentes
Qual é a principal finalidade dos cabeços de construção em canteiros de obras?
Postes de amarração de construção protegem trabalhadores e equipamentos de veículos. Eles criam limites claros e ajudam a controlar o tráfego. As equipes os utilizam para evitar acessos não autorizados e reduzir o risco de acidentes.
Com que frequência as equipes devem inspecionar os cabeços de construção?
As equipes devem inspecionar os cabeços pelo menos uma vez por mês. Eles precisam verificar se há danos, ferrugem, ou acessórios soltos. Inspeções regulares ajudam a manter a segurança e garantir a conformidade com os padrões da OSHA.
Os regulamentos da OSHA especificam o espaçamento exato para os postes de amarração?
OSHA não define um número específico. A maioria dos especialistas em segurança recomenda espaçar os cabeços não mais do que 48 centímetros de distância. Esta distância bloqueia veículos, mas permite que as pessoas passem com segurança.
As equipes podem usar postes de amarração de plástico em zonas de construção de tráfego intenso??
Os postes de amarração de plástico funcionam melhor em áreas temporárias ou de baixo impacto. Para zonas de alto tráfego ou de alto risco, as equipes devem escolher cabeços de aço ou concreto. Esses materiais oferecem melhor proteção contra impactos de veículos.
Que documentação as equipes devem manter para conformidade com a OSHA?
As equipes devem manter registros de inspeção, registros de manutenção, e detalhes de instalação. Estes documentos mostram que o site segue as regras da OSHA. Bons registros ajudam durante as auditorias e melhoram o gerenciamento geral da segurança.